Asthma is a long-term illness that personally affects the respiratory system and can impact people of any age around the globe. If not controlled it is life-altering and at worst life-threatening. Whether you are an asthma sufferer or a caregiver to a loved one with asthma, having this type of knowledge will go a long way in improving the situation. Here, the facts we will discuss include the definition of asthma, its signs, and causes, as well the functional approaches to its control.
What is Asthma?
Asthma is defined as a long-term disease that causes inflammation and narrowing of the airways that deliver oxygen to the lungs. This is a disease marked by chest discomfort, wheezing, breathlessness, and cough that is worse particularly at night or in the early morning. It is a chronic condition that can reach throughout a lifespan but manifests early in childhood.
Although much is not well understood regarding the causes of asthma, it is thought to be caused by genetics, environment as well as lifestyle factors. For instance, if one or both parents have asthma then the children are more likely to have the disease. Likewise, if a person is exposed to allergens, irritants such as pollen, smoke, or pollution, they are also at higher risk.
DrPro is a comprehensive healthcare solution designed to streamline patient care and clinic management. With its advanced features, including appointment scheduling, billing, and electronic medical records software, DrPro helps healthcare providers enhance efficiency and improve patient outcomes. By integrating tools for seamless communication, automated workflows, and robust data security, DrPro empowers clinics and hospitals to deliver exceptional care while reducing administrative burdens. Whether managing daily operations or ensuring compliance, DrPro stands as a trusted partner for modern healthcare needs
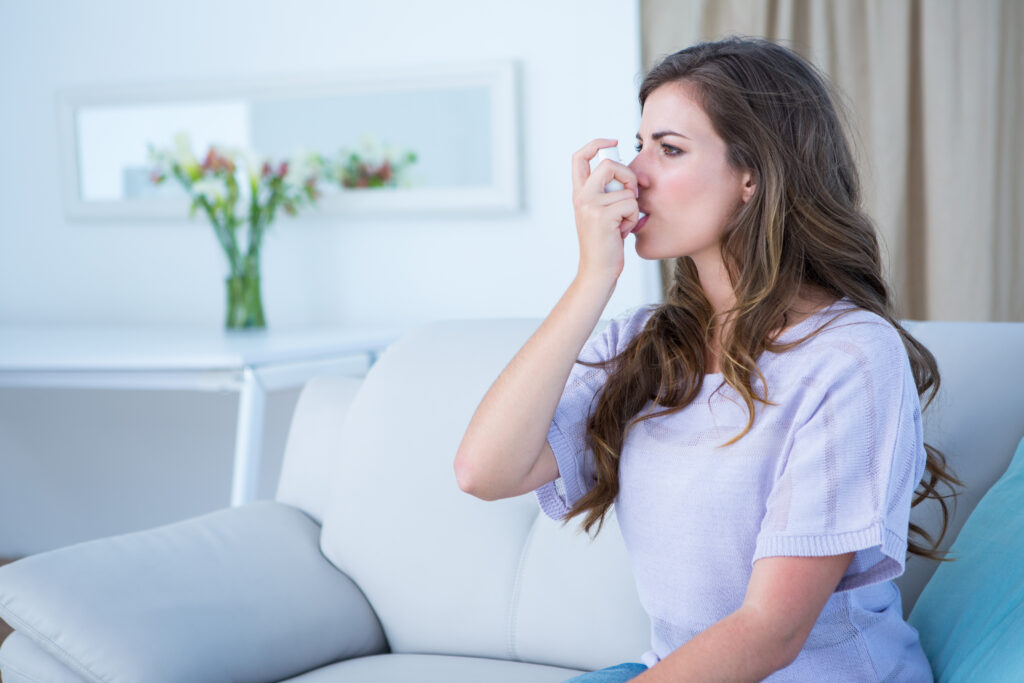

Asthma can feel like an enigma, but it doesn’t have to be a mystery. This guide breaks down asthma into portions, making it easier for everyone to understand. We’ll cover symptoms, triggers, and practical ways to manage this condition and live life to the fullest.
Understanding Asthma Symptoms
The signs of asthma are also diverse from one individual to another. For some, it is a condition manifested and possibly mild most of the time, for others it is an enduring chronic condition characterized by severe episodes. Common symptoms include:
Wheezing:
Breathing through the mouth, and worst it is associated with a whistling or squeaky sound.
Shortness of Breath:
Feeling out of breath like you’re struggling to breathe, or shortness of breath.
Chest Tightness:
A feeling of chest stiffness or heaviness.
Coughing:
Sometimes worse at night or early morning, a situation that may cause clear mucus appearance of the sputum.
These symptoms tend to be worse with allergens like dust, cold climate, or with the onset of exercise. For example, a child can develop a wheeze after he or she has gone to play in the field on a day when the pollen has risen. Pattern recognition in terms of the main symptoms can be useful in controlling and in some sense, even avoiding an asthma attack.
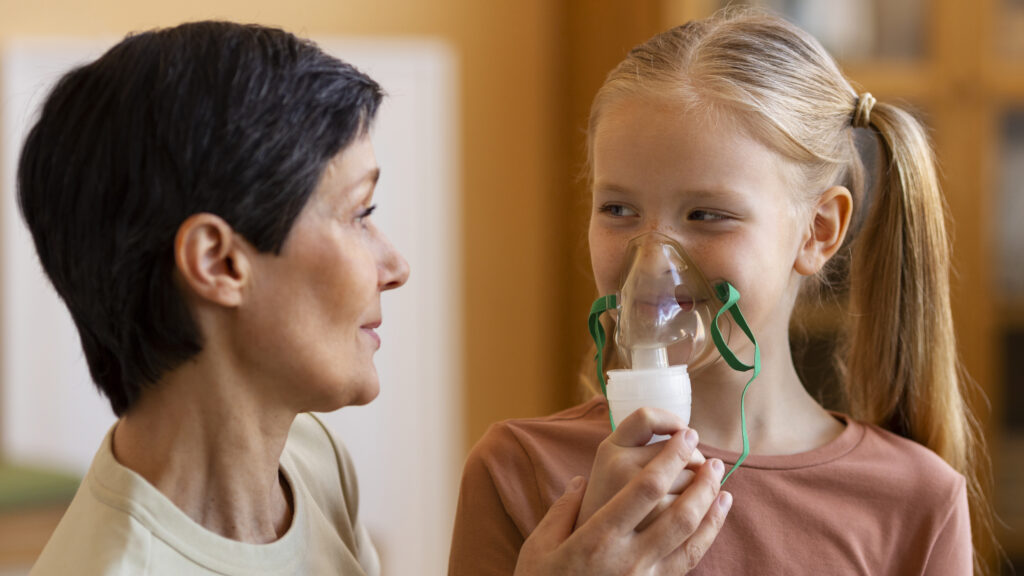
Diagnosis and Treatment
Asthma is generally diagnosed by using a patient’s history, physical examination, and some tests that may assess the lung’s function.
Medical History:
A doctor may inquire about symptoms of respiratory disease, history of asthma or allergies, and causes.
Spirometry:
This test determines the volume and flow rate of a forced exhalation, used to get information about the patient’s lung capacity.
Peak Flow Meter:
A handheld tool that helps find out the efficiency of your lungs during routine tasks.

Treatment Options
Asthma is a chronic illness that cannot be cured but for which there are numerous treatments when it comes to medicine and life changes. Common treatment options include:
Quick-Relief Medications:
Known often as rescue inhalers, these are used when an asthma attack is in progress. Examples include albuterol.
Long-Term Control Medications:
These are taken daily to reduce inflammation and to avoid any signs of this disease. Examples are ICSs and leukotriene antagonists.
Biologic Therapies:
In more serious cases of asthma, there are medications such as monoclonal antibodies that work on specific parts of the body’s immune system.
However, other treatments that are equally important involve a doctor to especially develop an asthma management plan.

Common Asthma Triggers
This means that knowing what causes your asthma is an important basis for managing the condition. Common triggers include:
Allergens:
This is due to pollens, dust mites, mold spores,s, and animal dander.
Irritants:
Smoke, smoke, heat, fumes, airborne particles, bad odors, effluence.
Respiratory Infections:
Cold weather, common cold, flu, sand inus infection among others.
Physical Activity:
It is however seen that the above symptoms can be triggered by intensive training especially when the weather is cold.
Weather Changes:
Cold air, drafts, or rapid change of climate.
Management Strategies
For asthma, there is a prevention strategy for symptomatic control and overall lifestyle enhancement. Here are some effective strategies:
1. Create an Asthma Action Plan
Talk with your doctor to create a specific plan on how to treat various conditions, for example, taking more doses of medication during an attack or knowing when to go for an emergency.
2. Avoid Triggers
This is why it is important not to be trigger-happy or trigger-shy but simply learn what causes one to trigger and stay away from them. For example, if pets cause issues then avoid them on the bed whether by removing them from the room or by using an encased pillow cover that is resistant to allergens.
3. Regular Medication Use
Take your long-term medicines as directed and keep your rescue inhaler on you always. One consequence of non-adherence is acute flares in disease symptoms.
4. Monitor Your Symptoms
Record your signs and your peak flow measurements to note any changes in your condition. Some patients benefit from keeping a diary of symptoms as a record or even having an app on their mobile phones.
5. Stay Physically Active
Fitness is good for individuals, but it should be independent of risks. Sometimes warm up before the exercise, and perform activities that do not seem to bring on the symptoms, for instance, swimming.
6. Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
Low-stress diets regular exercises, normal weight, and optimal sleep can help in improving the body’s immunity and lowering inflammation.
7. Attend Regular Checkups
Others recommend that even though your asthma may still appear stable, your doctor may need to make changes to your treatment plan.
Conclusion
Asthma is not an incurable disease and patients are empowered to live fully and actively through a lot of carefulness and hard work. Because of the symptoms of the disease, specific causes that could lead to it, and following the prescribed regimes, asthmatics can live normal, fulfilling, and active lives. Whether the recovery is as elementary as a child learning how to sequentially use an inhaler correctly or the grown-up learning techniques to control stress in order not to trigger flare-ups, it is all about small steps.
Noted! Let me know how I can assist with the updates for the DrPro wellness.
FAQs
Q1. Can asthma go away on its own?
Asthma can improve over time in some individuals, especially children, but it’s generally considered a lifelong condition.
Q2. Is asthma contagious?
No, asthma is not contagious. It’s a chronic condition influenced by genetic and environmental factors.
Q3. How can I tell if my asthma is severe?
Frequent symptoms, nighttime awakenings, or reliance on rescue inhalers may indicate poorly controlled or severe asthma. Consult your doctor.
Q4. Can exercise make asthma better or worse?
While intense exercise can trigger symptoms, regular physical activity with proper management can improve lung function and overall health.
Q5. Are there natural remedies for asthma?
While certain natural approaches, like using a humidifier or consuming anti-inflammatory foods, may help, they should not replace prescribed medical treatments.

